Atoms and Molecules class 9 notes of science chapter 3
Table of Contents-
1. Introduction
1.1 History
2. Laws of Chemical Combination
2.1 Law of conservation of mass
2.2 Law of constant proportions
3. Dalton's Atomic theory
4. What is an Atom?
4.1 Atomic mass of an element
4.2 How does an atom exist?
5. What are molecules?
5.1 Molecules of elements
5.2 Molecules of compounds
6. What is an ion?
6.1 Ions ( cation and anion)
6.2 Ionic compounds
6.3 Valency of an ion
7. Writing chemical formulae
7.1 Molecular mass
Introduction-
History-
- An Indian philosopher Maharishi Kanad postulated that if we go on to divide matter( padarth) into smaller and smaller particles. Ultimately, a stage will come beyond which we cannot further divide the matter( padarth). And, he called it 'parmanu'.
- Another Indian philosopher, Pakudha Katayama postulated that particles exist in combined form which is the reason behind the various forms of matter.
- Democritus and Leucipus also came to the same conclusion. Democritus called these indivisible particles " atoms".
Laws of Chemical Combination-
Law of conservation of mass-
- Given by Lavoisier in 1774
- It says that matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Law of constant proportions-- Given by Proust in 1779
- It says that a chemical compound always consists of the same elements combined together in a definite proportion by mass.
- For example, a water molecule always has two elements i.e. hydrogen and oxygen always combined in a fixed ratio of 1: 8 by mass. Irrespective of the source of water, whether tap water, river water, or distilled water, it always contains 1: 8 by mass.
Dalton's Atomic Theory-
The main postulates of atomic theory are-- All the matter is made up of extremely small tiny particles named ' Atoms'.
- Atoms are indivisible.
- Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
- Atoms of the same elements are identical in mass and chemical properties whereas it is different in different elements.
- Atoms form compounds on the combination of a small whole-number ratio.
- Given by Proust in 1779
- It says that a chemical compound always consists of the same elements combined together in a definite proportion by mass.
- For example, a water molecule always has two elements i.e. hydrogen and oxygen always combined in a fixed ratio of 1: 8 by mass. Irrespective of the source of water, whether tap water, river water, or distilled water, it always contains 1: 8 by mass.
Dalton's Atomic Theory-
- All the matter is made up of extremely small tiny particles named ' Atoms'.
- Atoms are indivisible.
- Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
- Atoms of the same elements are identical in mass and chemical properties whereas it is different in different elements.
- Atoms form compounds on the combination of a small whole-number ratio.
What is an Atom?
All the matter is made up of atoms just like all houses are made up of bricks, Thus, atoms are the building blocks of all the matter around us.
- Atoms are extremely small in size.
- The size of an atom is measured by its radius which is called ' atomic radius'.
- Atomic radius is measured in nanometres.
- Atoms are so small that we cannot see them under the most powerful optical microscope so, the most advanced type of electron microscope the Scanning Tunneling Microscope( STM) was used.
The atomic mass of an element-- The actual masses of the atoms of the elements are very, very small. However, carbon -12 isotope was chosen as the standard reference for measuring atomic masses.
- Carbon-12 was assigned an atomic mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units.
12 atomic mass unit ( amu) = 1 Mass of a carbon 12 atom 1 atomic mass unit ( amu) = 1/ 12 mass of a carbon -12 atom
How does an atom exist?- Atoms of most elements do not exist independently except for noble gases ( such as helium, neon, and argon, etc,)
- Atoms exist in 2 ways - in the form of molecules, or in the form of ions.
What is Molecules?
- A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together by the strong force of attraction.
- A molecule is capable of independent existence.
- A molecule can be formed in 2 ways- Molecules of elements and Molecules of compounds.
Molecule of elements-- The molecule of an element contains two or more of the same atoms chemically combined together.
- For example, the hydrogen molecule, nitrogen molecule, oxygen molecule, etc,
Molecule of compounds-- The molecule of a compound contains two or more dissimilar types of atoms chemically combined together.
- For example, carbon dioxide, water, etc,
What is an ion?
Compounds that are made of metals and non-metals that contain charged species. And these charged species are called " ions".There are 2 types of ions-- Cation ( Positively charged species)
- Anion ( Negatively charged species)
Positively charged species are known as cations.Negatively charged species are known as anions.
Ionic compounds -
The compound which is made up of both cation and anion is known as ionic compounds.For example, Sodium chloride Nacl [ Common Salt].
Valency of ions-
The valency of an ion is equal to the charge of the ion.
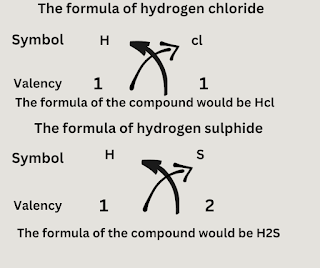
Writing Chemical formulae-
The chemical formula of a compound is simply a symbolic representation of its composition.Rules of writing chemical formulae- Write the symbol of each element that form the compound.
- Below the symbol of each element, write down its valency separately.
- Finally, cross over the valencies of the combining atoms to form a compound.
Molecular mass-
- For atoms, the term atomic mass is used, likewise, for molecules the term molecular mass is used.
- The molecular mass of a substance is the sum total of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance.
- For example- water molecule H2O = 2*1u + 16u = 2u + 16u = 18u
Co2 = 12u + 16*2 = 12u + 32u = 44u
- The actual masses of the atoms of the elements are very, very small. However, carbon -12 isotope was chosen as the standard reference for measuring atomic masses.
- Carbon-12 was assigned an atomic mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units.
12 atomic mass unit ( amu) = 1 Mass of a carbon 12 atom
- Atoms of most elements do not exist independently except for noble gases ( such as helium, neon, and argon, etc,)
- Atoms exist in 2 ways - in the form of molecules, or in the form of ions.
What is Molecules?
- A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together by the strong force of attraction.
- A molecule is capable of independent existence.
- A molecule can be formed in 2 ways- Molecules of elements and Molecules of compounds.
Molecule of elements-- The molecule of an element contains two or more of the same atoms chemically combined together.
- For example, the hydrogen molecule, nitrogen molecule, oxygen molecule, etc,
Molecule of compounds-- The molecule of a compound contains two or more dissimilar types of atoms chemically combined together.
- For example, carbon dioxide, water, etc,
What is an ion?
Compounds that are made of metals and non-metals that contain charged species. And these charged species are called " ions".There are 2 types of ions-- Cation ( Positively charged species)
- Anion ( Negatively charged species)
Positively charged species are known as cations.Negatively charged species are known as anions.
Ionic compounds -
The compound which is made up of both cation and anion is known as ionic compounds.For example, Sodium chloride Nacl [ Common Salt].
Valency of ions-
The valency of an ion is equal to the charge of the ion.
Writing Chemical formulae-
The chemical formula of a compound is simply a symbolic representation of its composition.Rules of writing chemical formulae- Write the symbol of each element that form the compound.
- Below the symbol of each element, write down its valency separately.
- Finally, cross over the valencies of the combining atoms to form a compound.
Molecular mass-
- For atoms, the term atomic mass is used, likewise, for molecules the term molecular mass is used.
- The molecular mass of a substance is the sum total of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance.
- For example- water molecule H2O = 2*1u + 16u = 2u + 16u = 18u
Co2 = 12u + 16*2 = 12u + 32u = 44u
- The molecule of an element contains two or more of the same atoms chemically combined together.
- For example, the hydrogen molecule, nitrogen molecule, oxygen molecule, etc,
Molecule of compounds-
- The molecule of a compound contains two or more dissimilar types of atoms chemically combined together.
- For example, carbon dioxide, water, etc,
What is an ion?
Compounds that are made of metals and non-metals that contain charged species. And these charged species are called " ions".
There are 2 types of ions-
- Cation ( Positively charged species)
- Anion ( Negatively charged species)
Positively charged species are known as cations.
Negatively charged species are known as anions.
Ionic compounds -
The compound which is made up of both cation and anion is known as ionic compounds.
For example, Sodium chloride Nacl [ Common Salt].
Valency of ions-
The valency of an ion is equal to the charge of the ion.
Writing Chemical formulae-
The chemical formula of a compound is simply a symbolic representation of its composition.
Rules of writing chemical formulae
- Write the symbol of each element that form the compound.
- Below the symbol of each element, write down its valency separately.
- Finally, cross over the valencies of the combining atoms to form a compound.
Molecular mass-
- For atoms, the term atomic mass is used, likewise, for molecules the term molecular mass is used.
- The molecular mass of a substance is the sum total of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance.
- For example- water molecule H2O = 2*1u + 16u = 2u + 16u = 18u
Co2 = 12u + 16*2 = 12u + 32u = 44u